Cloud Security: Not Just a Change of Location, But a Strategy Rebuild—How Secure is Your Data in the Cloud?

The New Home of Digital Data
The most impactful technological change of the last decade has been the rise of Cloud Computing. Everything—from personal photos and confidential office data to large software applications—has migrated to Cloud Storage and Cloud Services platforms. Due to its speed, convenience, and low cost, the cloud is now an essential part of our digital life.
However, beneath these advantages lies a massive challenge: Cloud Security. Many believe that the Cloud Providers (like AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) are solely responsible for all protection, but the reality is that securing data in the cloud is a Shared Responsibility. A minor error in configuration, a weakness in access control, or simple carelessness—even a small mistake can lead to millions in losses due to a Data Breach.
This blog post aims to cover the foundational concepts of Cloud Security, identify the main risks, and detail the global Best Practices for keeping your Cloud Data secure.
1. Core Concept of Cloud Security: Why Is It Different?
Cloud security is fundamentally different from traditional On-Premises security because your Infrastructure is no longer entirely under your control.
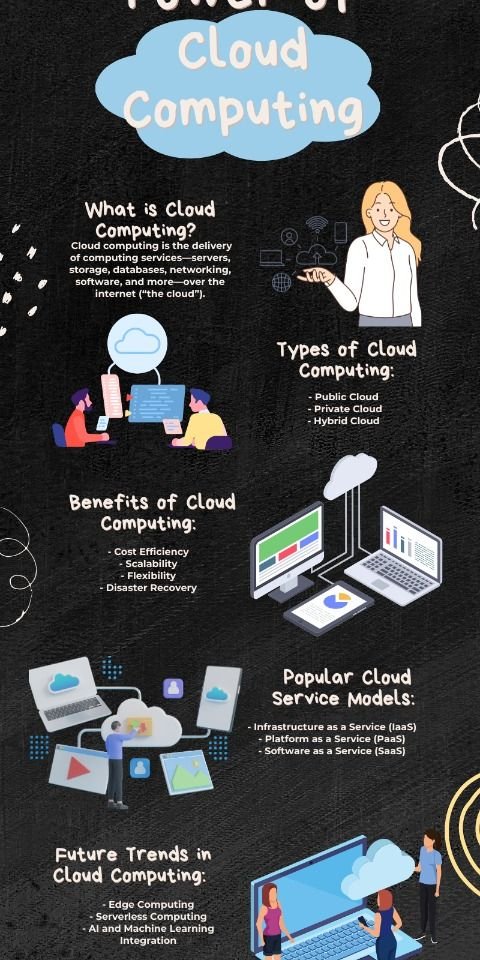
Types of Cloud Models:
Cloud services are typically divided into three main categories, and security control depends on the model you use:
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): (e.g., Virtual Machines) Here, you control the operating system and data security.
- PaaS (Platform as a Service): (e.g., Development Platforms) Here, you control application and data security.
- SaaS (Software as a Service): (e.g., Google Workspace, Microsoft 365) Here, you only control data and user access.
The Shared Responsibility Model:
This is the most critical aspect of cloud security. The core principle is:
- Cloud Provider is Responsible for ‘Security of the Cloud’: This includes the physical security of the data centers, hardware, and the global network infrastructure.
- The Customer is Responsible for ‘Security in the Cloud’: This includes your Cloud Data, user Access Control, Encryption, and proper Misconfiguration avoidance.
The majority of cloud security incidents and data breaches result from the customer’s failure in handling ‘Security in the Cloud’.
2. Major Risks and Vulnerabilities in Cloud Protection
The three most common security risks encountered in the cloud environment are discussed below:
A. Misconfiguration: The Leading Cause of Data Leaks
This is the number one vulnerability in Cloud Security. It is more a human error than a technical fault.
- Example: Accidentally setting an AWS S3 bucket to ‘Public Access’. Consequently, any internet user can access the stored data (such as customer personally identifiable information or server backups) without a password. Thousands of Data Breach incidents occur due to this single type of error.
B. Weak Identity and Access Management (IAM)
In the cloud, all security relies on Identity and Access Management (IAM) instead of physical barriers.
- Risk: Weak passwords, insufficient Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), or granting Over-Privileged Access to a user who doesn’t need it—all these create opportunities for hackers to penetrate the system. Once a hacker steals a user’s identity, they can easily take control of the entire network.
C. Unsecured APIs
Most Cloud Services are managed through Application Programming Interfaces or APIs.
- Risk: If these APIs are not properly secured, hackers can exploit the vulnerable API to steal data or run unauthorized commands within your Cloud Computing environment. Therefore, Cloud Application Security is now vital.
3. Best Practices for Securing Cloud Data
To mitigate risks and protect data in the cloud environment, it is essential to follow these advanced practices:
1. Prioritize Encryption:
- Data-at-Rest Encryption: Ensure all data stored in your cloud is Encrypted. Every Cloud Provider offers encryption tools; utilizing them is mandatory.
- Data-in-Transit Encryption: Encrypt data transmission between the cloud and the user using protocols like SSL/TLS.
2. Implement Zero Trust Policy:
- The Zero Trust Architecture is an essential model for the cloud environment. Its meaning is: “Never trust, always verify.”
- Continuously verify every access request from every user and device, whether they are inside or outside the network boundary.
3. Utilize Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM):
- CSPM (Cloud Security Posture Management) tools automatically scan your cloud configurations to check for any Misconfiguration. For instance, checking if any storage bucket is mistakenly set to ‘Public’. Through Automation, these tools significantly reduce the probability of human error.
4. Strict IAM and MFA Enforcement:
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Mandate MFA for all cloud accounts, especially for administrator accounts.
- Principle of Least Privilege: Grant users only the minimum access strictly necessary for their work. Avoid granting excessive permissions. This principle reduces the impact of Insider Threats and Cyber Attacks.
5. Regular Backup and Disaster Recovery Planning:
- Backup Strategy: Even when storing data in the cloud, take regular Backup copies and store them in a way that protects them from Ransomware attacks.
- Recovery Plan: Create a clear Disaster Recovery Plan and regularly test it, ensuring a quick return to normal operations in case of a major incident.
Conclusion: Cloud Control is in Your Hands
Cloud Computing has immensely enhanced our digital capabilities, but its protection is an ongoing process. It is crucial to remember that the ultimate responsibility for Data Security in the cloud rests with you—not solely with the Cloud Provider.
Cloud Security is no longer just an ‘option’; it is an Essential Strategy. By adopting practices like Encryption, Zero Trust, and CSPM (Cloud Security Posture Management), you can safeguard your data in this new digital home.
We hope these advanced guidelines help you meet the challenges of the cloud environment. Stay safe and always keep control of your data.